Navigating the Landscape of Online K-12 Education: A Guide to Jobs and Opportunities
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Online K-12 Education: A Guide to Jobs and Opportunities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Online K-12 Education: A Guide to Jobs and Opportunities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Online K-12 Education: A Guide to Jobs and Opportunities

The realm of education is experiencing a significant transformation, with online learning rapidly gaining prominence. This shift has created a diverse array of opportunities in the K-12 sector, offering a range of career paths for individuals passionate about fostering learning in a digital environment. This article delves into the various roles within online K-12 education, highlighting the unique skills and qualifications required, the benefits these positions offer, and the future trajectory of this evolving field.
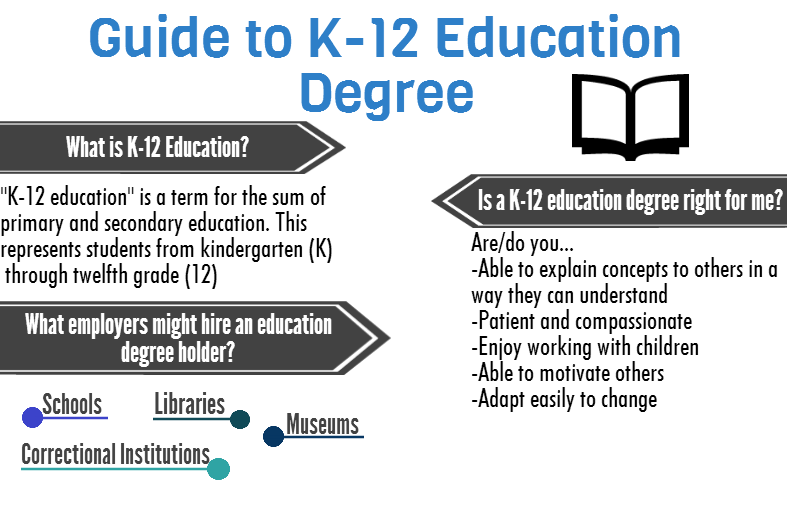
Understanding the Online K-12 Ecosystem
Online K-12 education encompasses a wide spectrum of learning models, from fully virtual schools to blended learning programs that integrate online and in-person instruction. This variety translates into a diverse range of job roles, each contributing to the overall success of the educational experience.
Key Roles in Online K-12 Education:
1. Teachers and Instructors:
- Curriculum Development: Teachers in online K-12 settings play a pivotal role in designing and adapting curricula to suit the digital learning environment. They must possess strong pedagogical knowledge, coupled with the ability to translate traditional classroom practices into engaging online modules.
- Instructional Design: Online teachers are adept at creating interactive lessons, utilizing multimedia tools, and implementing innovative teaching strategies to maintain student engagement and facilitate effective learning.
- Assessment and Feedback: Adapting assessment methods to the online environment requires proficiency in using online tools, understanding the nuances of digital assessment, and providing timely and constructive feedback.
- Communication and Collaboration: Online teachers are skilled communicators, fostering positive relationships with students through online platforms, and collaborating effectively with parents, administrators, and fellow educators.
2. Instructional Designers and Developers:
- Content Creation: Instructional designers work closely with teachers and subject matter experts to develop engaging and effective online learning materials. They create interactive modules, videos, simulations, and other digital resources that enhance the learning experience.
- Technology Integration: These professionals are well-versed in educational technology, ensuring seamless integration of various tools and platforms into online courses, and optimizing their use for maximum impact.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Instructional designers are proficient in using and managing LMS platforms, configuring courses, tracking student progress, and ensuring the smooth functioning of the online learning environment.
3. Educational Technology Specialists:
- Technical Support: These professionals provide technical assistance to teachers, students, and administrators, troubleshooting issues with online platforms, software, and hardware.
- System Administration: They maintain and manage the infrastructure of online learning platforms, ensuring system security, data integrity, and optimal performance.
- Technology Integration: Educational technology specialists work with teachers and instructional designers to integrate new technologies into the curriculum, maximizing their educational impact.
4. Curriculum Specialists:
- Alignment and Assessment: Curriculum specialists ensure that online courses align with state and national standards, adapting existing curricula to the digital learning environment and developing appropriate assessments to measure student progress.
- Content Development: They may also contribute to the development of online learning materials, collaborating with teachers and instructional designers to ensure content quality and relevance.
5. School Administrators:
- Leadership and Vision: Online school administrators provide leadership and guidance, setting the vision and direction for the school, fostering a positive learning environment, and ensuring the smooth operation of the online programs.
- Student Support: They oversee student services, including enrollment, attendance, counseling, and special needs support, ensuring equitable access and support for all students.
- Staff Development: Administrators play a crucial role in professional development for teachers and staff, ensuring they are equipped with the skills and knowledge to excel in the online learning environment.
The Benefits of Online K-12 Education Jobs
1. Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: Online education jobs offer a high degree of flexibility, allowing individuals to work from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be particularly attractive to those seeking a better work-life balance or who prefer a remote work environment.
2. Diverse Career Paths: The online K-12 sector presents a wide range of career opportunities, catering to individuals with diverse skillsets and interests. From teaching and curriculum development to technology integration and administration, there are roles to suit various passions and expertise.
3. Continuous Learning and Development: The rapid pace of innovation in online education necessitates continuous learning and professional development. Individuals in this field have access to a plethora of resources, workshops, and conferences, enabling them to stay abreast of emerging trends and technologies.
4. Impactful Work: Working in online K-12 education allows individuals to make a direct and positive impact on the lives of students, empowering them to learn and achieve their full potential. The ability to reach learners across geographical boundaries and diverse backgrounds adds a unique dimension to this work.
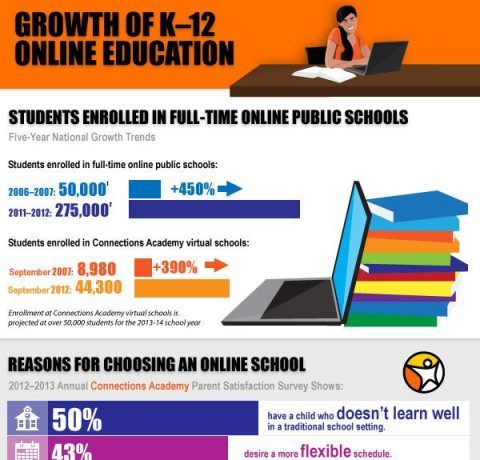
5. Growing Demand: As online learning continues its rapid growth, the demand for qualified professionals in this field is expected to increase significantly. This presents a promising career path with ample opportunities for advancement and career growth.
FAQs about Online K-12 Education Jobs:
1. What qualifications are required for online K-12 education jobs?
Qualifications vary depending on the specific role. Most positions require a bachelor’s degree, with a master’s degree often preferred for leadership roles. Teachers typically need state-issued teaching licenses, while instructional designers may have backgrounds in education, instructional technology, or related fields.
2. What are the salary expectations for online K-12 education jobs?
Salaries vary based on experience, location, and specific role. Teachers and instructors typically earn salaries comparable to their traditional classroom counterparts. Instructional designers and educational technology specialists may earn higher salaries, reflecting the specialized skills and technical expertise required.
3. What are the challenges of working in online K-12 education?
Challenges include maintaining student engagement, adapting to evolving technologies, and ensuring equitable access to resources and support for all students. Effective communication and collaboration are essential to overcome these challenges and create a successful learning environment.
4. How can I prepare for a career in online K-12 education?
Individuals interested in this field should pursue relevant degrees, obtain teaching licenses (if applicable), and develop skills in instructional design, educational technology, and online communication. Networking with professionals in the field and gaining experience through internships or volunteer work can also be beneficial.
Tips for Success in Online K-12 Education Jobs:
1. Embrace Technology: Stay abreast of emerging educational technologies and integrate them effectively into your teaching or work practices. Develop a strong understanding of learning management systems and online collaboration tools.
2. Foster Engagement: Develop innovative teaching strategies that cater to the unique needs of online learners. Use interactive multimedia resources, gamification, and other engaging techniques to create an interactive and stimulating learning environment.
3. Prioritize Communication: Maintain clear and frequent communication with students, parents, and colleagues. Utilize various communication channels, including email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and online forums.
4. Seek Professional Development: Continuously enhance your skills and knowledge through professional development opportunities, workshops, and conferences. Stay informed about the latest trends and research in online education.
5. Build a Strong Network: Connect with other professionals in the field through online communities, professional organizations, and conferences. Networking can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and career opportunities.
Conclusion:
The landscape of online K-12 education is dynamic and evolving, presenting exciting opportunities for those seeking rewarding and impactful careers. By understanding the diverse roles within this field, developing relevant skills, and embracing the challenges and rewards of this innovative learning environment, individuals can contribute to the future of education and empower students to reach their full potential in the digital age.

/GettyOnlineEducationH1200-56aa2e115f9b58b7d0019183.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Online K-12 Education: A Guide to Jobs and Opportunities. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!